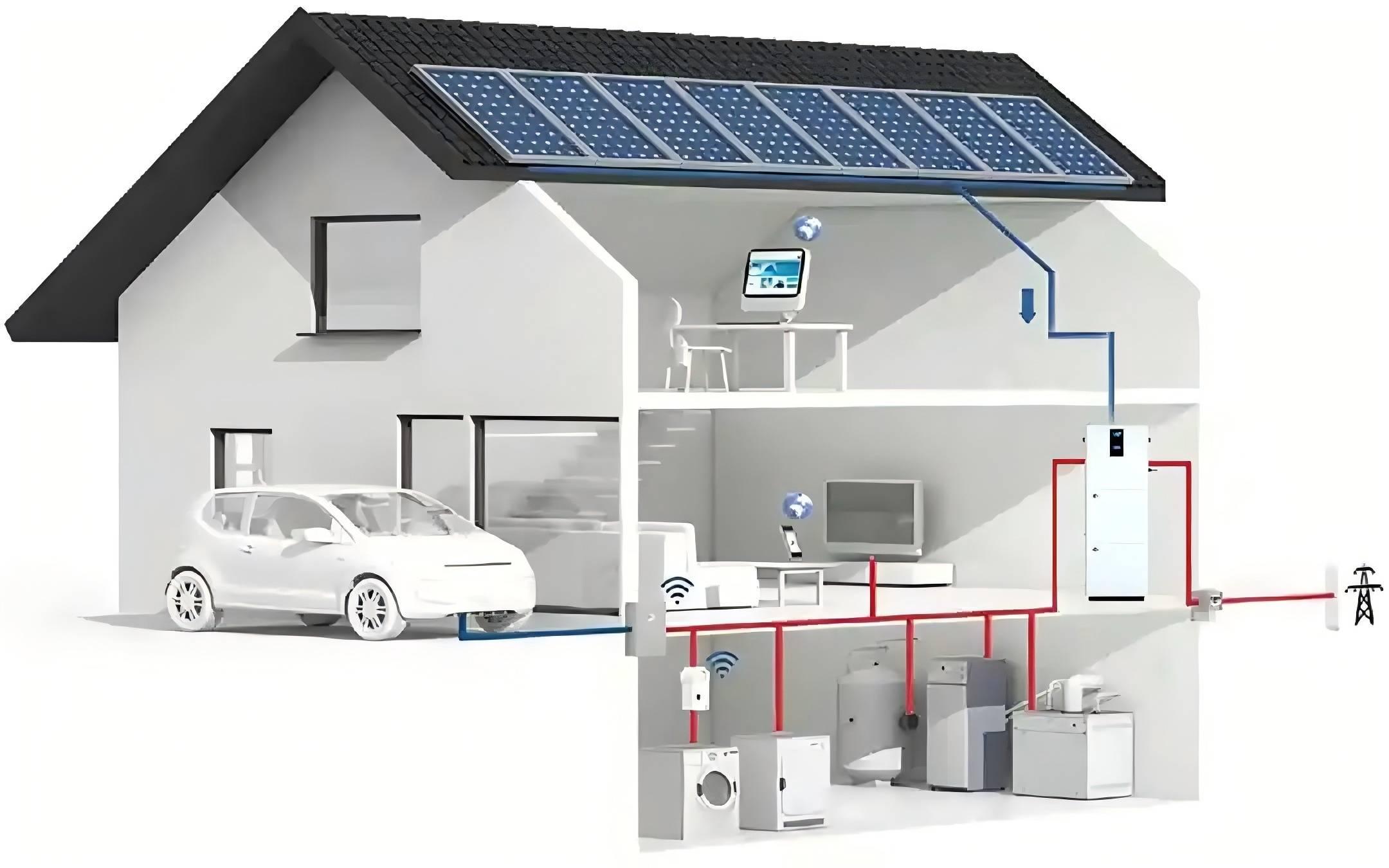
With the rapid development of renewable energy and the growing popularity of smart homes, home energy storage systems have become an essential part of household energy management as a vital energy storage solution. The service life of these systems has always been a key point of interest. This article will delve into the working principles, common types, service life, and methods to extend the lifespan of home energy storage systems, aiming to provide readers with a comprehensive understanding and valuable reference.
1. Working Principle of Home Energy Storage Systems
A home energy storage system refers to the use of energy storage devices (such as lithium batteries, sodium-sulfur batteries, supercapacitors, etc.) to store electrical energy for release when needed, achieving efficient household energy management and utilization. Its working principle primarily includes two processes: energy storage and energy release. During energy storage, the system collects and stores energy generated from renewable sources such as solar or wind power. During energy release, the system uses inverters and other devices to convert the stored energy into alternating current (AC) for household use.
2. Common Types of Home Energy Storage Systems
Currently, the main types of home energy storage systems include lithium battery storage systems, sodium-sulfur battery storage systems, and supercapacitor storage systems. Lithium battery storage systems are the most common type, due to their high energy density, long cycle life, and low self-discharge rate. Sodium-sulfur battery storage systems, with their high-temperature tolerance and long-cycle life, are widely used in specific environments. Additionally, supercapacitor storage systems are gaining attention for their fast charge/discharge characteristics and long lifespan.
3. Service Life of Home Energy Storage Systems
The service life of a home energy storage system refers to the time it can function normally, an important indicator of its performance. Generally, the service life of a home energy storage system is closely related to the cycle life of its battery. The cycle life represents the number of charge-discharge cycles a battery can complete under specific depth of discharge and charging conditions, and it's a key measure of battery longevity. Typically, lithium batteries can reach several thousand cycles, while sodium-sulfur batteries and supercapacitors have even longer cycle lives.
The service life of home energy storage systems is influenced by several factors, such as depth of discharge, temperature, and charge/discharge rates. In actual use, if the system undergoes frequent deep discharges or rapid charging and discharging, its lifespan may be reduced. Additionally, high-temperature environments accelerate battery aging, thereby shortening the service life of the energy storage system.
4. Methods to Extend the Service Life of Home Energy Storage Systems
To address the shorter lifespan of home energy storage systems, certain measures can be taken to extend their service life. First, set a reasonable depth of discharge, avoiding frequent deep discharges to reduce battery cycle counts and extend lifespan. Second, control the operating temperature of the storage system to avoid prolonged exposure to high temperatures, which can slow down battery aging. Additionally, choosing an appropriate charge/discharge rate and avoiding frequent rapid charging and discharging are also essential for extending the service life of home energy storage systems.
In summary, as a critical energy storage device, home energy storage systems play an essential role in household energy management. The longevity of these systems directly impacts their performance and cost-effectiveness. Understanding the working principles, common types, and service life of home energy storage systems is important for enhancing household energy management and prolonging the service life of the equipment. We hope this article provides valuable guidance and reference for readers.