China's energy storage industry poised for strong growth
287% is the ratio of Bloomberg New Energy Finance's forecast of China's installed energy storage capacity in 2025 relative to China's national target in 2025
250GW / 701GWh is Bloomberg New Energy Finance's forecast of China's cumulative installed energy storage capacity by the end of 2030
10%-13% is the ratio of annual energy storage capacity (in GW) for time-shifted energy applications to large-scale ground-mounted photovoltaic and wind project capacity in China from 2023 to 2030
China is in the midst of an energy storage development boom, with cumulative installed capacity expected to reach 250GW/701GWh by 2030, almost 23 times the level at the end of 2022. While policy mandates are likely to be the driver of installations in the short term, improving business models and falling costs are likely to drive more economics-led installations beyond 2025. China will continue to lead the global uptake of installed energy storage in this decade.
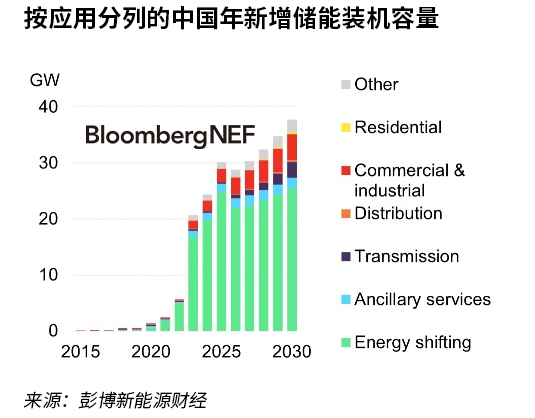
China has overtaken the US to become the world's largest energy storage market in 2022. China's new energy storage installations accelerate in 2023 and could add as much as 21GW/44GWh of installed energy storage capacity this year, double the cumulative capacity installed through the end of 2022. China's total installed capacity could reach 86GW/196GWh by 2025, almost triple the target set in China's Implementation Program for the Development of New Energy Storage (excluding pumped storage).
Despite this strong growth, the development of battery storage in China is still based on a policy-driven approach rather than an economic one. For any new renewable energy project to receive a grid connection license, renewable energy developers must build or lease new or leased energy storage installations. These projects are hardly ever used, resulting in very low utilization rates and little economic sense.
After 2025, the economics of energy storage projects may increase with the development of new business models and the gradual marketization of China's electricity market. Battery storage projects may gain access to new revenue streams, such as capacity payments, energy arbitrage, peak shaving and payments for ancillary services.
Energy time-shift applications account for nearly 80% of new energy storage projects in 2023, driven by significant increases in installed wind and PV capacity. Customer-side services, transmission and distribution, and ancillary services contribute 7%, 2%, and 5% of the total, respectively.
We expect commercial and industrial applications to play a larger role in the coming years, driven by widening peak-to-valley tariff spreads and improved economics. We estimate that C&I storage now makes economic sense in 23 out of a total of 31 provinces in mainland China. Meanwhile, unless subsidies are introduced, household energy storage is likely to remain marginal, mainly to meet electricity resilience needs in rural areas.
Next:The U.S. local energy storage industry, but also "climbing over the hurdles"
Previous:What is the use and significance of lithium-ion battery energy storage system?
