World Most Advanced Battery Energy Storage System Replace Hawaii, Last Coal Plant

In a groundbreaking leap towards sustainability, Plus Power’s Kapolei Energy Storage (KES) facility in Hawaii has commenced commercial operations. As Hawaii bids farewell to its last coal plant, KES takes center stage, offering an innovative solution to maintain grid reliability amid the transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy.
The plant is considered as the most advanced grid-scale battery energy storage system (BESS) in the world. BESS are rechargeable batteries that can store energy from various sources and discharge it when necessary. The system is composed of one or more batteries often used to balance the traditional grid, provide backup power, and enhance grid stability.
The project, developed and owned by Houston-based Plus Power, began operations before Christmas. It features 158 Tesla Megapacks with a total capacity of 185 megawatts of instantaneous discharge. This capacity matches the power output of the retired coal plant but offers a faster response time of 250 milliseconds.
Hawaii’s Clean Energy Revolution
The state of Hawaii decided to shut down its last coal plant on September 1, 2022. This decision marked a significant step in the state’s commitment to achieving 100% renewable energy for electricity by 2045.
The challenge then arose of ensuring grid reliability with a mix of renewable sources subject to weather fluctuations.
The Kapolei Energy Storage System addresses this challenge by absorbing excess power from the grid during renewable generation peaks and delivering it during high-demand evening hours.
Brandon Keefe, Executive Chairman of Plus Power, expressed pride in contributing to Hawaii’s renewable energy goals and enabling the transition. Keefe particularly noted that:
“This is a landmark milestone in the transition to clean energy… This project is a postcard from the future — batteries will soon be providing these services, at scale, on the mainland.”
Despite facing construction setbacks, including disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic and the project’s remote location, KES is now operational. It outpaces several other renewable energy projects in replacing the retired coal plant’s capacity.
The gigantic battery project aligns with Hawaii’s commitment to becoming a leader in clean energy adoption and grid transformation.
Beyond Energy: Kapolei’s Multifaceted Grid Stabilization
The Kapolei Energy Storage system operates differently from traditional coal plants, requiring a new framework to replicate essential grid functions. While the old coal plant provided energy, capacity, and grid services, the battery directly replaces the latter two aspects.
Kapolei’s 185 megawatts of instantaneous discharge capacity matches the coal plant’s power output. Plus, it offers grid services, such as synthetic inertia and fast frequency response, to stabilize the grid in real time.
Although the battery’s 565 megawatt-hours of storage cannot directly replace the coal plant’s energy production, it collaborates with solar energy sources to enhance clean renewable energy integration into the grid.
KES enables Hawaiian Electric to reduce the curtailment of renewables by an estimated 69% for the first 5 years. This minimizes the waste of surplus clean electricity.
Additionally, the battery provides black-start capability, allowing it to restart the grid in case of a complete outage due to disaster.
According to Keefe, Kapolei is considered the most advanced battery energy storage facility globally because of its multifaceted capabilities. These include capacity, grid services, and black-start functionality. He further added that since the project connects to 3 other power plants, the battery “can be AAA to jump-start those other plants”.
Lithium Powers the Clean Energy Transition
Lithium-ion batteries are seen to be the solution for helping the world to transition to clean, renewable energy sources. This is crucial to meet the critical 1.5 degrees Celsius scenario by 2050, otherwise known as the Net Zero.
Companies and governments are turning to battery energy storage systems (BESS) to achieve their sustainability goals. Research suggests that the market for BESS in the U.S. alone will grow to over $15 billion in 2027.
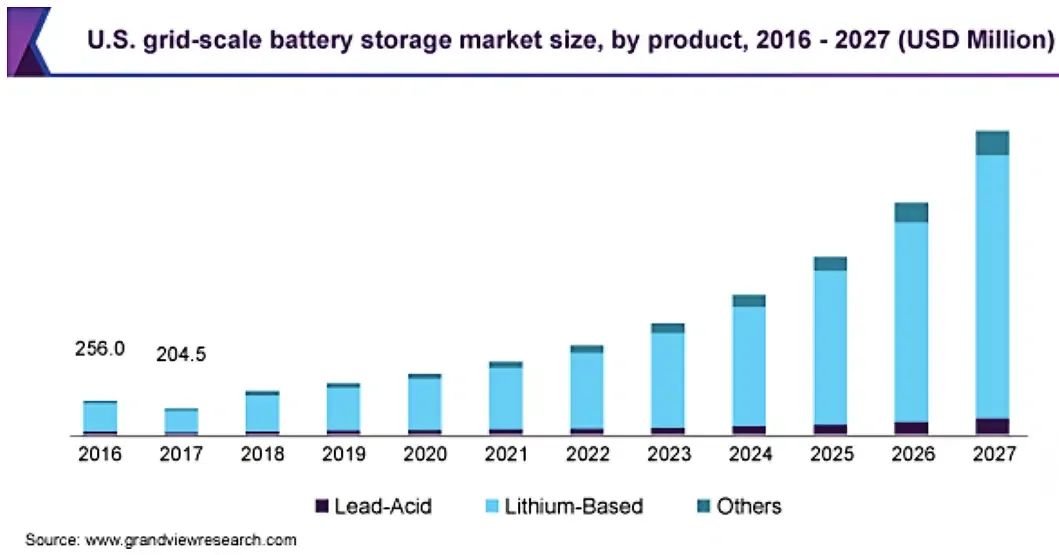
The surge in the use and future demand for renewable energy will further lead to global grid-scale BESS market growth. As per the International Energy Agency’s projections, renewables will account for over 90% of global electricity capacity expansion from 2022-2027. With that, growth seems to be quicker in locations where renewables are also expanding faster than average.
Hawaii’s Kapolei Energy Storage system represents a groundbreaking model for a reliable clean-energy grid, addressing the challenges of transitioning from fossil-fueled plants to renewable sources.
The KES battery project uses 158 Tesla Megapack 2 XL lithium iron phosphate batteries, each roughly the size of a shipping container.
In comparison to California’s grid battery fleet, which constitutes 7.6% of the state’s grid capacity, Kapolei alone represents about 17% of Oahu’s peak capacity, highlighting its central role in maintaining grid stability.
Looking ahead, Kapolei’s success underscores its significance in achieving U.S. climate goals by phasing out fossil fuels from the electric grid. As one of the first real-world instances of successfully transitioning grid functions, the model established by Kapolei provides valuable insights for scaling similar grid services nationwide, offering a blueprint for the future of sustainable grid solutions.
Next:Over 1,700 MW Solar and 1,300 MW Battery Storage Across Arizona, California, and Nevada
Previous:Neoen shut down Australian solar-plus-storage plant after 7 years

