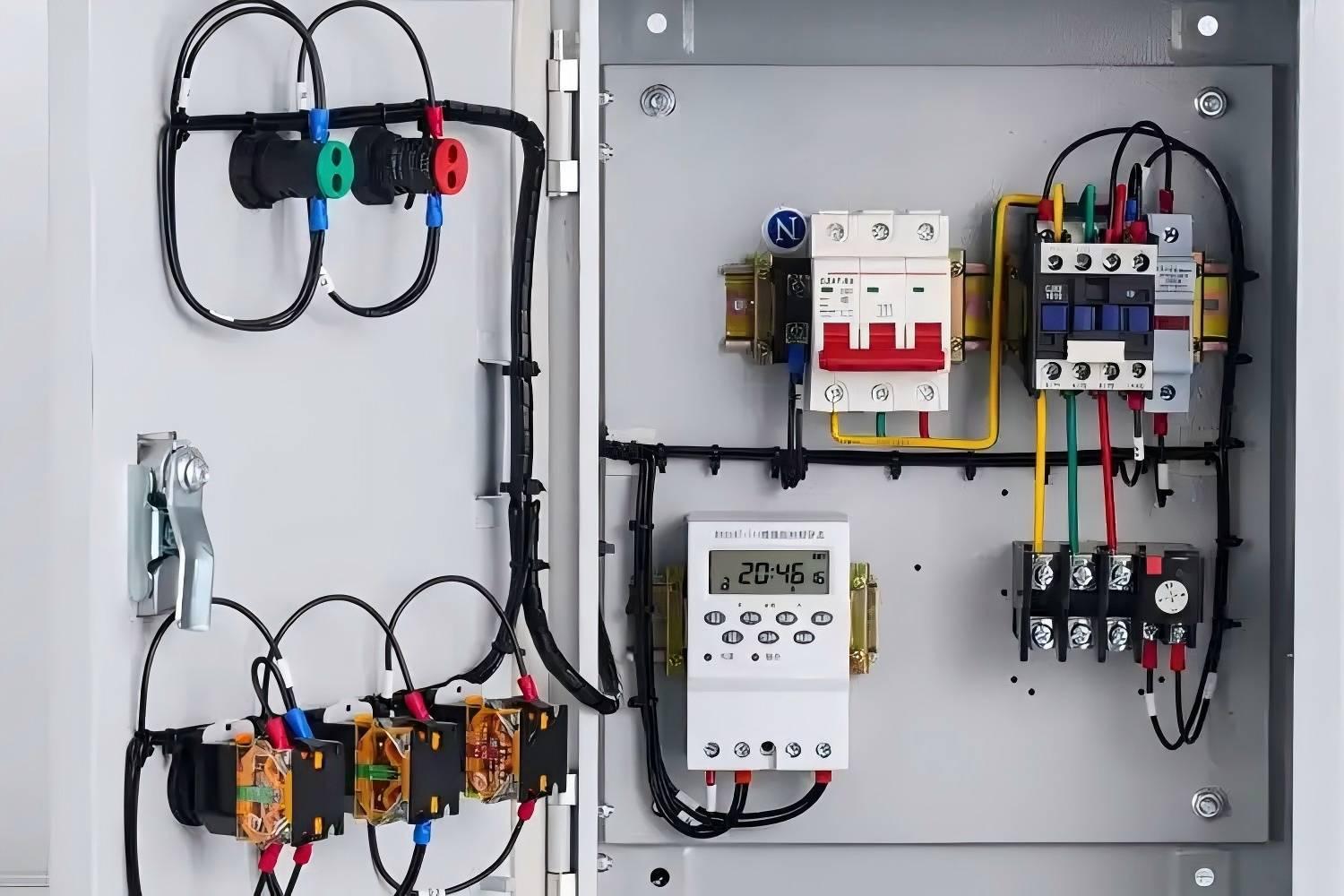
Relay protection is a critical technique used in power systems to detect faults or abnormal conditions, trigger alarm signals, or directly isolate and remove faulty sections of the system. Its main goal is to prevent faults from spreading and to protect both equipment and the overall system.
How It Works
A relay protection system typically consists of three components: the measurement unit, the logic unit, and the execution unit. The system works by monitoring changes in electrical parameters (such as current, voltage, and power) during normal and fault conditions.
Under normal operating conditions, electrical parameters like current, voltage, and power remain stable. The relay protection device continuously monitors these values and compares them with predefined settings. When the system is operating normally, the measured values stay within safe limits, and the protection device stays inactive.
However, when a fault occurs, such as a short circuit, ground fault, or overload, these electrical parameters change dramatically. For example, a short circuit causes a sudden surge in current and a sharp drop in voltage. The protection system's measurement unit quickly detects these changes and passes the data to the logic unit.
The logic unit then analyzes the measurements according to preset rules to determine if a fault is present. If a fault is confirmed, the logic unit sends an action signal to the execution unit.
The execution unit, upon receiving the signal, performs the necessary action, such as tripping the circuit or sending an alarm. This isolates the faulty section, preventing further damage and ensuring the safe, stable operation of the power system.
Common Types of Relay Protection
There are several types of relay protection, each designed to address different fault conditions. Some of the most common include:
1. Overcurrent Protection
This type of protection detects when current increases beyond a safe level during a fault. For example, if equipment becomes faulty and causes a short circuit, the current spikes. The overcurrent protection device detects the surge and trips the circuit, preventing further damage to the system.
2. Overvoltage Protection
This protection is triggered when the voltage exceeds a safe threshold. Overvoltage can occur due to factors like lightning strikes or system faults. For instance, during a thunderstorm, lightning may strike a power line and cause an overvoltage. The overvoltage protection device quickly responds to prevent equipment damage.
3. Differential Protection
Used mainly for protecting transformers, generators, and other critical equipment, differential protection compares the current entering and leaving the device. If a significant difference is detected, indicating a fault, the system will isolate the equipment to prevent further damage. For example, if a transformer develops an internal fault, differential protection will detect the imbalance and disconnect it from the network.
4. Distance Protection
Distance protection determines fault location based on impedance, which is calculated from voltage and current measurements during a fault. The system compares this impedance with preset values to decide whether to trip the circuit, based on how far the fault is from the protection device.
Key Functions of Relay Protection
1. Fault Detection and Isolation
Relay protection quickly detects faults such as short circuits or ground faults and isolates the affected section from the rest of the system. This prevents the fault from spreading, ensuring that the rest of the power network remains operational.
2. Protecting Equipment
By acting swiftly, relay protection prevents damage to electrical equipment caused by conditions like overcurrent or overvoltage. This helps prolong the lifespan of equipment and reduces the need for costly repairs.
3. Maintaining System Stability
Prompt isolation of faults helps keep the power system stable, minimizing the impact on power supply to customers and ensuring the reliability of the system.
4. Preventing Escalation of Accidents
In cases of severe faults, relay protection plays a key role in preventing the situation from worsening, avoiding potential safety hazards such as fires or explosions.
Relay protection is essential for the safe and reliable operation of power systems. It ensures that faults are quickly detected and isolated, protecting both equipment and the broader system, and ultimately providing stable power to support economic and social activities.