Thermal management of electric vehicle batteries: Current status and future of liquid cooling technology.
With the transformation of the global energy structure and the promotion of environmental protection awareness, electric vehicles have become an important development direction of the automotive industry. Battery is the "heart" of electric vehicles, its performance and life directly affect the performance and reliability of the vehicle.
In this context, the importance of battery thermal management systems has become increasingly prominent, and liquid cooling technology, as one of the efficient heat dissipation methods, has become one of the key technologies to improve the performance of electric vehicles, is facing the dual challenges of technological progress and cost control, and has gradually become a research hotspot in the industry.
Overview of liquid cooling technology
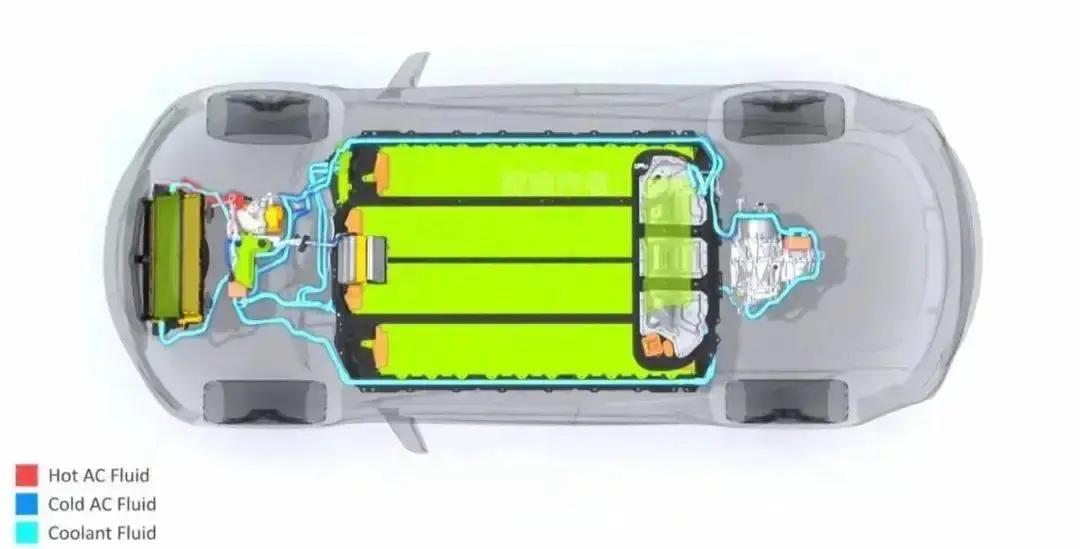
Liquid cooling technology refers to the circulation of liquid media (such as water, glycol solution, etc.) to take away the heat generated by the battery, so as to maintain the battery in the appropriate temperature range, this technology is particularly important in high-performance electric vehicles, because it can effectively extend the battery life, improve energy density and charging efficiency.
Compared with traditional air cooling systems, liquid cooling systems have the advantages of higher heat transfer efficiency, smaller volume and weight, and lower noise.
Key technology
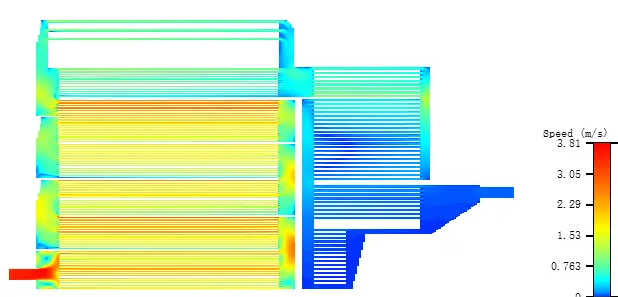
The design and manufacture of liquid cooling systems is a comprehensive engineering that requires engineers to possess interdisciplinary knowledge and skills, as well as a deep understanding of new materials, processes, and technologies. A number of key technologies need to be involved, including but not limited to:
01 runner design
The flow channel design is the core of the liquid cooling system, which directly affects the flow characteristics and heat exchange efficiency of the coolant. By utilizing computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation technology, engineers can simulate the flow of coolant in the flow channel and predict and analyze heat exchange efficiency. Combined with the structural topology optimization method, the optimal flow channel geometry can be found to achieve higher heat conductivity and lower fluid resistance.
02 Material selection
The choice of materials has a direct impact on the performance of the liquid cooling system. Usually, liquid cooling plates choose metal materials with high thermal conductivity, such as aluminum or copper, which can effectively conduct heat from the heat source and quickly carry it away through the coolant. However, in addition to thermal conductivity, the corrosion resistance and mechanical strength of the material are also factors that must be considered when designing, and these characteristics ensure that the liquid cooling system can maintain long-term stability and reliability in a variety of operating environments.
03 Pump and radiator
The pump and radiator are the "heart" and "lungs" of the liquid cooling system, which together maintain the circulation of the coolant and the dissipation of heat. As the "power source" of the liquid cooling system, the key to the selection of the pump is its efficiency and reliability, which needs to ensure that it can provide stable flow under various working conditions. The design of the heat sink needs to consider cost-effectiveness while ensuring the heat dissipation performance to achieve the best cost performance.
04 Control Policy
The control strategy is very important for the effective operation of the liquid cooling system. Through the precise control algorithm, the flow of coolant and the working parameters of the radiator can be dynamically adjusted according to the actual temperature and working state of the heat source, so as to ensure that the temperature of the battery or other key components is stable within the best working range and prevent overheating or undercooling.
05 Manufacturing process
The advanced manufacturing process directly affects the performance and reliability of the liquid cooling system. Precision manufacturing of liquid-cooled plates can be achieved using 3D printing technology and micro-channel processing technology, which makes the size and shape of the flow channels more precise, thereby improving the compatibility and heat dissipation efficiency of the entire system. At the same time, advanced manufacturing processes also help reduce manufacturing defects and improve product consistency and reliability.
Technical challenges and solutions
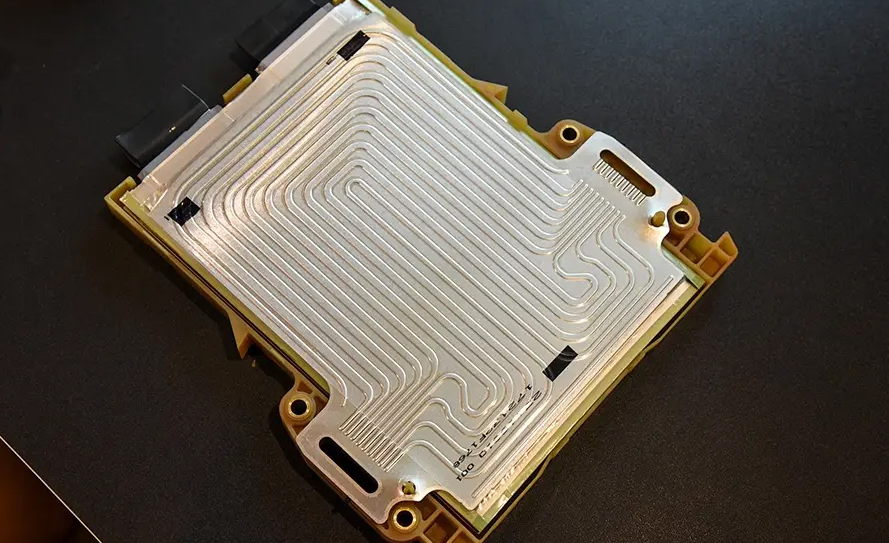
Although liquid cooling technology has significant advantages, it still faces many challenges in practical applications. First, the complexity of liquid cooling systems requires precise engineering design and high-quality manufacturing processes. Secondly, the choice of coolant and the sealing of the circulation system are critical to the long-term stability of the system. In addition, as electric vehicles expand to the mass market, how to reduce the cost of liquid cooling systems and make them more affordable is also an urgent problem to be solved.
To address these challenges, researchers and engineers are exploring multiple solutions. For example, heat exchange efficiency can be improved through the use of new high-thermal conductivity materials and optimized flow channel design. At the same time, the intelligent thermal management system can dynamically adjust the cooling strategy according to the actual working state of the battery, thereby improving energy efficiency and reliability.
Application status and development trend

With the popularity of electric vehicles, the liquid cooling system market is experiencing rapid growth. On the one hand, high-end electric vehicle brands will continue to adopt liquid cooling systems to maintain their market competitiveness; On the other hand, with the reduction of technology costs, the middle and low-end markets will gradually accept liquid cooling systems. In addition, with global policy support and subsidies for new energy vehicles, the market demand for liquid cooling systems will further expand.
At present, many high-end electric vehicle brands have begun to adopt liquid cooling systems, such as Porsche and Audi, and Tesla's Model S and Model X have adopted liquid-cooled battery systems, which achieve efficient thermal management through the cooling plate and coolant circulation system integrated into the battery pack.
With the continuous expansion of the electric vehicle market, in the future, liquid cooling technology is expected to develop in the following directions:
01 Integrated design
In order to simplify the system structure, and reduce the volume and weight, the liquid cooling system will tend to be integrated with the battery pack design.
02 Intelligent control
By integrating more sensors and adopting advanced control algorithms, precise control of battery temperature and failure prediction are achieved.
03 Application of environmental protection materials
In order to reduce the environmental impact, the liquid cooling system will be more environmentally friendly and recyclable materials.
04 Cost optimization
Through material innovation and manufacturing process improvement, the cost of liquid cooling systems is reduced and its market competitiveness is improved.
Liquid cooling technology for electric vehicle batteries is the key to ensuring battery performance and life, and its technological innovation and market opportunities are receiving high attention from the industry. With the continuous advancement of technology and the reduction of costs, liquid cooling systems will play an increasingly important role in the electric vehicle industry. Through interdisciplinary cooperation and technology integration, we expect liquid cooling technology to bring more efficient, reliable, and environmentally friendly thermal management solutions to electric vehicles in the future.
Next:Battery Energy Storage System Field: Wave of New Energy Storage Containers
Previous:Solid State Battery, Disruptive Technology for New Energy Vehicles