Lithium-ion batteries are integral to modern technology, powering everything from smartphones and laptops to electric vehicles. Their high energy density and long lifespan make them an attractive choice, but they also come with certain risks, including the potential for fires. Understanding the causes of these fires from various perspectives and implementing effective prevention strategies is crucial for maintaining safety. This comprehensive guide explores the causes of lithium-ion battery fires and provides detailed prevention tips from multiple angles.
1. Technical Perspective
Overcharging
Cause: Overcharging occurs when a battery is charged beyond its maximum voltage limit, which can cause the electrolyte inside the battery to break down and generate excessive heat. This can lead to thermal runaway, where the battery heats up uncontrollably and may catch fire.
Prevention:
- Use Smart Chargers: Modern devices and chargers are equipped with overcharge protection. Ensure your charger is compatible with your device and has built-in safety features.
- Avoid Extended Charging: Unplug devices once they reach 100% to prevent overcharging, especially if the device or charger lacks automatic shut-off features.
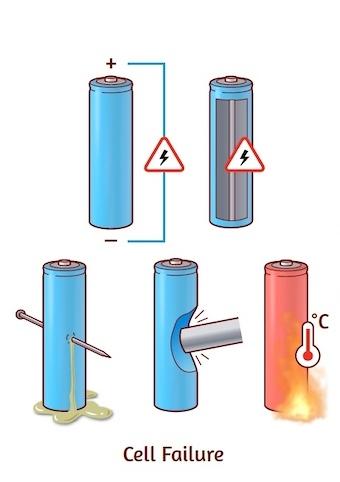
Internal Short Circuits
Cause: Internal short circuits occur when there is unintended contact between the positive and negative electrodes inside the battery. This can be caused by manufacturing defects, physical damage, or degradation of the battery components.
Prevention:
- Quality Control: Purchase batteries from reputable manufacturers who adhere to strict quality control measures.
- Handle with Care: Avoid dropping or puncturing batteries to prevent internal damage that could lead to short circuits.
Thermal Runaway
Cause: Thermal runaway is a chain reaction within the battery that causes it to heat up uncontrollably. It can be triggered by factors like overcharging, internal short circuits, or exposure to high temperatures.
Prevention:
- Temperature Management: Keep devices and batteries in environments with stable, moderate temperatures. Avoid exposing them to direct sunlight or heat sources.
- Ventilation: Ensure devices have adequate ventilation to dissipate heat during use.
2. Environmental Perspective
Extreme Temperatures
Cause: Exposure to extreme temperatures, whether too hot or too cold, can affect the performance and safety of lithium-ion batteries. High temperatures can accelerate chemical reactions within the battery, while low temperatures can lead to reduced efficiency and potential freezing.
Prevention:
- Store Properly: Keep batteries and devices in a cool, dry place, away from direct heat sources or extreme cold.
- Avoid Hot Environments: Do not leave devices in cars on hot days or near heat-generating appliances.
Humidity
Cause: High humidity can lead to moisture ingress, which can corrode battery components and increase the risk of failure or fire.
Prevention:
- Protective Cases: Use protective cases that shield batteries from moisture and dust.
- Dry Storage: Store batteries and devices in a low-humidity environment to prevent corrosion and degradation.
3. User Practices Perspective
Physical Damage
Cause: Physical damage, such as punctures, dents, or crushing, can compromise the integrity of the battery, leading to short circuits and overheating.
Prevention:
- Protective Measures: Use cases and covers to protect devices from physical impacts.
- Handle with Care: Avoid dropping or mishandling devices to minimize the risk of physical damage.
Improper Usage
Cause: Using batteries or devices in ways not intended by the manufacturer can lead to safety issues. This includes using incorrect chargers, operating devices in extreme conditions, or attempting unauthorized modifications.
Prevention:
- Follow Instructions: Adhere to the manufacturer’s guidelines for charging, usage, and maintenance.
- Use Approved Accessories: Only use chargers and accessories that are approved by the device manufacturer.
4. Manufacturing and Design Perspective
Manufacturing Defects
Cause: Defects in the manufacturing process can lead to faulty batteries with inherent risks. Issues such as weak separators, contaminants, or poor assembly can increase the likelihood of battery failures.
Prevention:
- Certification: Choose batteries from reputable brands that provide certifications and adhere to industry standards.
- Quality Assurance: Ensure that the battery and device have passed rigorous quality assurance tests.
Design Flaws
Cause: Design flaws in batteries or devices can contribute to safety issues. This might include inadequate thermal management or insufficient protective circuitry.
Prevention:
- Research: Invest in devices with well-reviewed safety features and design.
- Stay Updated: Keep informed about recalls or updates related to battery safety and device design.
5. Lifecycle and Aging Perspective
Battery Degradation
Cause: As batteries age, their performance deteriorates, which can increase the risk of overheating and fire. Degradation includes loss of capacity, increased internal resistance, and chemical changes.
Prevention:
- Regular Replacement: Replace batteries that show signs of significant degradation, such as reduced battery life or physical swelling.
- Monitoring: Track the age and condition of batteries and replace them as needed before they become a safety risk.
Conclusion
Lithium-ion batteries are a cornerstone of modern technology, but their potential fire risks necessitate careful handling and proactive safety measures. By examining the causes of battery fires from technical, environmental, user practices, manufacturing, and lifecycle perspectives, you can implement a comprehensive approach to prevention. Prioritize quality, follow best practices for usage and storage, and stay informed about the latest safety recommendations to ensure the safe and efficient use of lithium-ion technology.